Coal-based power generation increases in Pakistan under CPEC Projects
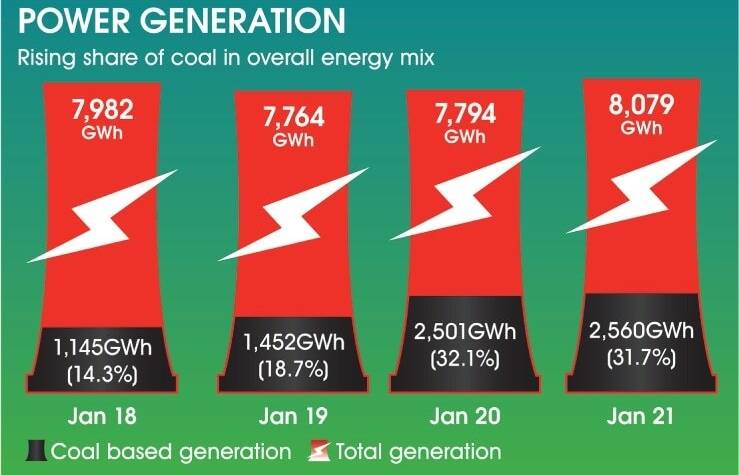
Coal-based power generation in January 2021 has risen to a seven-month high of 2,560-gigawatt hours (GWh) as total generation from different fuels increased by 3.7 per cent, under CPEC-related energy projects. In the last five years, Pakistan has aggressively pursued coal power under CPEC, increasing coal-based capacity from negligible to 4,620 megawatts. With seven other coal-based projects under construction, the country expects to add 4,590 megawatts by the end of 2026. Sheikh Mohammad Iqbal, a power-sector consultant based in Lahore, says the maximum utilisation of coal-based power is critical for slashing the overall cost of generation for countries like Pakistan.
LAHORE: Coal-based power generation in January rose to the seven-month high of 2,560 gigawatt hours (GWh) as total generation from different fuels increased by 3.7 per cent to 8,079 GWh from 7,794 GWh a year ago and by 2.5 per cent from 7,880 GWh from the previous month.
Coal power generation in the country peaked at 2,581 GWh in July last year before sliding back to 1,095 GWh in November. As a ratio of total generation in any given month in the last three years since the beginning of 2018, the share of coal power rose its highest of just below 32pc in January 2021. According to data, share of coal generation in the country’s total electricity output bottomed to 9.2pc in September 2018.
In the last five years Pakistan has aggressively pursued coal power under the multi-billion-dollar China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) initiative as well as outside it, increasing coal-based capacity from negligible to 4,620 megawatts. With seven other coal-based projects under construction, the country expects to add 4,590 megawatts by the end of 2026.
Coal power has increased by above 62pc to 15,262 GWh during the first seven months of the current fiscal year from 9,395 GWh during the same period in FY19, underscoring growth in its capacity and utilisation because of fuel price considerations. Its share in overall generation during the period July-January has risen from 12.9pc in FY19 to around 20pc this year in spite of 8.7pc increase in the cost of coal-based generation year-on-year to Rs6.47 per KWh last month on global coal prices.
An Arif Habib analyst, Rao Aamir Ali, said the share of coal power during winter increases because of reduction in hydel generation and closure of gas-based plants due to the shortage of the fuel. He pointed out that the share of coal power in the country’s generation will likely double in the years to come as new plants come online over the next six years to end 2026.
Sheikh Mohammad Iqbal, a power-sector consultant based in Lahore, is glad to see the increasing share of coal power in the country’s total power generation. “I am of the firm view that maximum utilisation of the coal-based power is critical for slashing the overall cost of generation. It is good for the economy of countries like Pakistan even though some may oppose coal power because of its potential impact on the environment.
“But they should remember that the coal power technology has improved a great deal and it no longer can be regarded dirty fuel when it comes to producing electricity from it. I would say coal is much cleaner fuel for electricity generation than furnace oil.”
China charts new growth path as ‘Two Sessions’ launch 15th Five-Year Plan era
BEIJING: China signalled a new phase in its economic strategy as the country’s top legisla…